Life in the modern age is very fast, and with changing lifestyle, there is a drastic observable change which we can notice in our lives. Stress, tension, work pressure, failed relationships, unhealthy eating habits, sluggishness towards work, all have become a part of our daily routine. As a result of which people face high blood pressure, mental disturbance, cardiac problems, digestive system problems and miserable family life.
So there is an utmost need to pause our lives for a moment and let all our worries get away. As it is rightly said that we become what we think, so to think aptly is very much needed. Pranayama helps us to regulate our breathing which in turn controls our lives thus bringing a positive change in our lives.
Pranayama is a combination of 2 words; Prana means “Breath” and Ayama means “Control.” Even simple breathing patterns can have a powerful impact on our lives. So, check out the following breathing exercises for a healthy body.
1. Natural Breathing

Natural breathing is a simple breathing exercise where all you have to do is breathe normally with both your nostrils. Inhale and exhale with as much speed as you can. You can even do it for as long as you feel like doing it. It helps your body to relax.
2. Basic Abdominal Breathing

Abdominal Breathing is a type of breathing exercise where you are required to lie down on your yoga mat and breathe. Feel your breath, as you inhale your abdomen area should rise while it should flatten as you exhale. Keep a check on the breath as there should be a minimal moment of your chest. You will feel a sense of calmness after practising Abdominal Breathing Pranayama. Shoulder movement should be minimised.
3. Thoracic Breathing

Thoracic breathing is a type of pranayama where the involvement of your abdominal area is minimised and is replaced by engaging your chest. This breathing technique requires more energy as compared to abdominal breathing. It lowers stress, tension and helps the body to obtain more oxygen.
4. Clavicular Breathing
This type of breathing involves the movement of the shoulder and your clavicle area(collarbone) to rise when you inhale while keeping the rest of the body motionless. Clavicular breathing provides oxygen to the top third of your lungs. It can be practised at any time and especially when you are under stress or anger to calm down your nerves. Its primary focus is to increase the amount of oxygen intake, correct poor breathing habits and gain control of your breath.
5. Yogic Breathing

Yogic breathing is a 3 step process which starts with breathing through the lower abdomen, covering the mid-torso and finally reaching the upper chest and shoulders. Follow the same 3 steps while releasing breath in the reverse order, i.e. exhaling from the chest through the torso and finally the lower abdomen. This completes one cycle. Yogic Breathing releases stress, anxiety, nervousness, refreshes our mind and brings our body to a balanced state.
6. Deep Breathing

Deep breathing is a slow, deep and rhythmic pattern of breathing through the nose, holding your breath for a while and releasing it. Deep breathing helps to detoxify your body, increases blood count, releases tension, relaxes the mind, strengthens the immune system, uplifts mood, boosts energy level and improves stamina. Make sure you practice it every day for at least 5 to 10 minutes.
7. Fast Breathing

Unlike Kapalbhati and Bhastrika, fast breathing does not involve forceful inhalations and exhalations. Here, both the inhalations and exhalations are of equal durations. In fast breathing, we approximately inhale and exhale 100 breaths per minute. It relaxes your nerves, increases oxygen flow, frees your mind from emotional clutter, provides immunity to the organs and is beneficial for the people suffering from sinusitis.
8. Viloma Pranayama

Viloma pranayama is a breathing exercise in which regular inhalations and exhalations are interrupted thus increasing the overall duration of breathing. It can be performed while sitting as well as lying. Viloma helps to calm down the brain nerves, relaxes mind and body and bring lightness to your body. Pregnant women and people suffering from high blood pressure should avoid doing it.
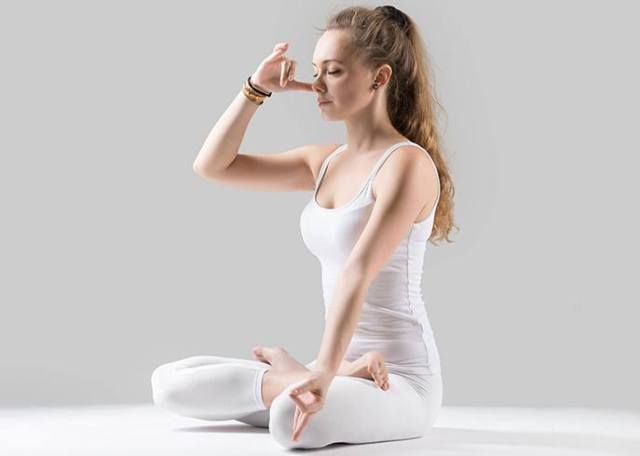
9. Alternate Nostril Breathing

Alternate Nostril Breathing Pose popularly known as Nadi Shodhan pranayama, comes up with the benefits to cures a frequent headache, lung cleaning, improves sleep quality, mental relaxation, regulates body temperature, promoting hearing ability, relieves tension and anxiety and boosts metabolism. This breathing exercise involves alternating by blocking one nostril while breathing from the opposite one.
10. Sheetali And Sitkari Pranayama
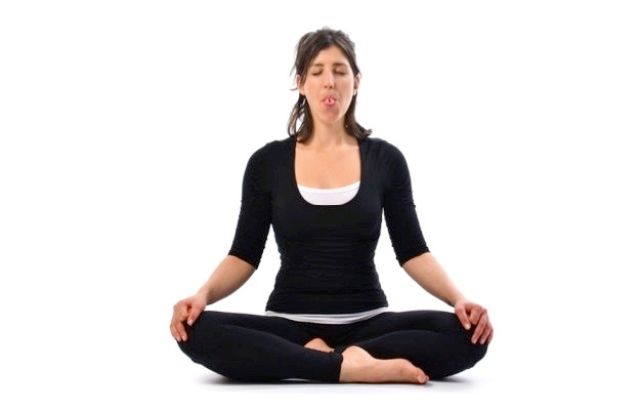

Sheetali and Sitkari are the words derived from Sanskrit means “cold” and “sipping” respectively. This two pranayamas cools down the body temperature and bring it to normal. Both are beneficial for the endocrine glands to function properly. These pranayamas help to remove excess of heat from our body, controls hunger, hunger and is very useful for brain muscles as it soothes them.
11. Ujjayi Pranayama

Ujjayi pranayama is popularly known as “ocean breath”. Ujjayi means “Victorious Breath”. While you inhale and exhale, the ocean-like sound is produced because of the friction of air in your throat. Try to sync your breaths as you breathe in and breathe out. It helps to focus your mind, increases concentration, improves thyroid glands, lowers the risk of cardiac arrests and is best suitable for the asthma patients.
12. Bhramari Pranayama
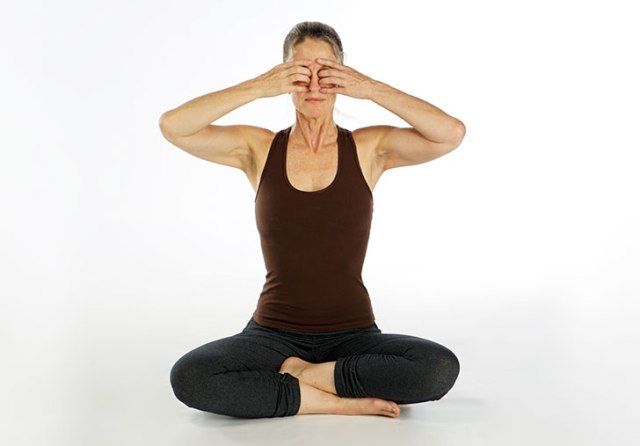

Bhramari Pranayama, also known as Humming Bee Breathing is a useful technique to cure hypertension. It is also one of the most effective breathing exercises to destress our mind from all the unnecessary clutter which keeps on revolving in our mind. With the continuous and determined practice of this activity, one can surely get useful results related to poor concentration, anxiety, high blood pressure, migraines and lack of confidence. And the best part of this yoga pose is you can do it anywhere and at any time, be at work or home.
13. Bhastrika Pranayama

Bhastrika is a Sanskrit word which means to breathe like a bellow; therefore sometimes it is also known a bellow breathing. In bellow breathing, as you breathe in you have to feel as if you are taking in the positivity and as you breathe out you are releasing all your worries, tension and negativity. It purifies the blood, provides strength to your immune system, heats up our body and relaxes your mind.
14. Surya Bheda Pranayama
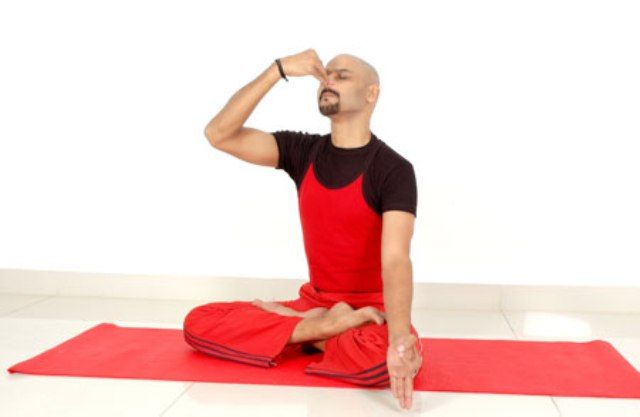

Surya Bheada Pranayama is also known as Right Nostril Breathing. It is a technique where you breathe in through the right nostril, hold your breath for a while and breathe out through the left nostril. For increasing the benefits of Surya Bheda, you have to perform it in ratios or batches (1,4,2 or 2,8,4), i.e. bhedas. It is beneficial for depression, reduces anxiety and mental illness. As it produces so much of heat in the body thus helps in burning all the ailments.