Table of Contents
Prophet Muhammad

Prophethood is a crucial principle in Islam. It is based on the notion that Allah has sent a sequence of prophets to guide humanity in the right direction.
According to Islam, Allah wants to help people live respectable lives, so he teaches them how to do so. Muslims believe that prophets are conduits for Allah’s revelations. The prophets are not revered because Allah is the sole true God. Rather, they are held highly.
Muhammad took birth in the city of Mecca. The Prophet Muhammad became Allah’s messenger after his first experience of revelation in the year 610. Muhammad had gone to the mountains near Mecca during Ramadan and meditated in a cave when the Angel Jibril appeared. Muhammad was forty years old and couldn’t read at the time, but Jibril told him to recite three times.
Muslims believe Allah chose Muhammad as his Prophet because he was a kind and wise man who genuinely cared about his people.
Allah continued to deliver his message to the Prophet for the next 23 years. His close colleagues and disciples wrote down the revealed teachings of the Prophet Muhammad. According to Muslim tradition, Allah’s final words to Muhammad were: This day, I have finalized their religion for themselves, for which I have completed all my favor upon you, and selected Islam as your faith. Muhammad is the final Prophet sent by God. He is also regarded as the Seal of the Prophets. This indicates that the Quran is the final revelation from God. Because the Prophet Muhammad is so significant to Muslims, they strive to live in his footsteps, and the Hadith and Sunnah are essential sources of authority for Muslims to guide their lives.
Five Pillars of Islam
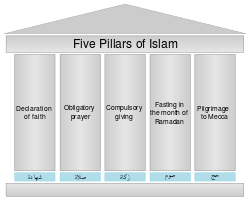
1) Faith: Islam’s core doctrine is that “there is no god but God, and Muhammad is God’s Messenger.” This Arabic phrase frequently appears in architecture and a variety of things, including the Qur’an, Islam’s sacred book of divine revelations. By uttering this phrase with conviction, one becomes a Muslim.
2) Prayer: Muslims often pray five times a day, in the morning, noon, mid-afternoon, sunset, and after dark, in the direction of Mecca. The first chapter of the Quran (sura) is recited during prayer, which is sometimes done on a small rug or mat designated for this purpose. Muslims can pray individually or in groups at a mosque led by an imam (prayer leader). Men gather at the mosque for noonday prayer on Fridays; women are welcome but not required to attend. Following the prayer, the imam will always pray and speak about such a religious subject before giving the lecture-based upon a Quranic chapter.
3) Alms: Islamic law requires Muslims to give a certain percentage of their wealth to people in their society who are in need. As a ministerial responsibility and to protect the benefits of charity, many kings and wealthy Muslims build mosques, drinking fountains, hospitals, schools, and other institutions.
4) Fasting: During Ramadan, the ninth month of the Islamic calendar, all healthy adult Muslims are expected to restrict from eating anything and drinking anything during the daylight hours. They renew their appreciation and knowledge of all that God has provided in their lives, especially the Quran, which was revealed for the first time this month. During Ramadan, they share the poor’s hunger and thirst as a reminder of their religious commitment to help those who are less fortunate.
5) Pilgrimage: Every Muslim must pay at least one visit to Mecca, in modern-day Saudi Arabia, if their health and means allow. In the heart of Mecca’s Haram Mosque sits the Kaba, a cubical edifice with black embroidered hangings. Muslims believe it is the house built for God by Abraham (Ibrahim in Arabic), and they pray in front of it (qibla). Since the first time of the Prophet Muhammad, believers from all over the world have gathered around the Kaba in Mecca, on the eighth and twelfth day of the Islamic calendars of the final month.
Depiction of Prophet Mohammad

This category includes several depictions of the Prophet Muhammad. While these images are rare, they are not unheard of in the Islamic world, where there were (and still are) many different perspectives on portraying the Prophet and humanity in general. The communities that made the paintings featured here were among the first to accept the Prophet’s portrayal, and their sentiments varied significantly from place to place and throughout history.
All the images appear in the biographies of the Prophet and his family for the world and the local history, and descriptions of Muhammad’s celestial voyage Mi’raj, as well as literary literature, and were commissioned by Muslims for Muslims. They serve a different purpose in each situation. They serve as visual parallels to written praises of the Prophet in biographies and histories. They have also served as a visual analogue to be reported as praises of the Prophet in literary writings. At the start of a book, a picture of the Prophet Muhammad bestows the highest level of grace and sanctity on the work. As a result, depictions of him were prevalent, especially in the Islamic world’s eastern areas.
After the Death of Prophet Mohammad

When Muhammad left for heaven in 632, he had not appointed a successor. According to the Shi’a, only individuals with direct ancestry to the Prophet could appropriately manage the Muslim community. They believed that ‘Ali, Muhammad’s closest blood relative, should be their next leader (caliph). On the other hand, the Sunnis thought that the Prophet’s successor should be chosen by consensus. Thus they elected three of his closest associates as leaders of the Muslim community, known as the Rightly Guided Caliphs (Abu Bakr, ‘Umar, and ‘Uthman), with Ali following them as the fourth caliph.
Today, the Islamic community is still divided into Sunni and Shi’i branches. Sunnis worship all four caliphs, whilst Shi’is recognize ‘Ali as the first spiritual leader. The rift between these two factions has resulted in differences in worship and political and religious ideals. Sunnis are the majority and dominate the Muslim world, while Shi’is are primarily located in Iran and Iraq, with substantial populations in Bahrain, Lebanon, Kuwait, Turkey, Pakistan, and Afghanistan.
Affirmations

1. I seek Allah’s guidance whenever I need it, and I accept responsibility for my own life.
2. When I’m feeling overwhelmed, I try to keep things simple.
3. I recall that my life aims to worship Allah.
4. I put my faith in Allah’s kindness.
5. First and foremost, I pray to Allah.
6. My Prophet is one of my favorites.
7. I try to remember Allah as much as I can.
8. When I want to make a difference in my life, I start with myself.
9. Exams are an unavoidable part of life. When they arrive, I am patient.
10. I am eternally grateful to Allah.
11. When I am grateful, Allah blesses me with more.
12. I make use of my logic.
13. Every night I always make a list of three things for which I am forever grateful.
14. With patience and prayer, I seek Allah’s assistance.
15. More than any other quality, Allah stresses His Mercy.
16. I try to stay away from fights.
17. My difficulties exist to draw me closer to Allah.
18. The next planet takes precedence for me.
19. I am, without a doubt, a believer.
20. I recall Allah’s mercy.
21. When I pray to Allah, He prays back to me.
22. My significant states of being are gratitude and patience.
23. I take measures and put my faith in Allah.
24. When I’m unhappy, I think of people who have less.
25. I only say positive things.
26. I accept all the responsibility for my life and seek Allah’s guidance whenever I need it.
27. When I’m feeling stressed, I try to keep things as simple as possible.
28. My life’s purpose, I recall, is to adore Allah.
29. I put my trust in Allah’s mercy.
30. I pray to Allah first and foremost.
31. One of my favorite books is My Prophet.
32. I make every effort to remember Allah.
33. I start with myself when I want to make a difference in my life.
34. Exams are a part of life that cannot be avoided. I am patient when they arrive.
35. Allah is the source of my eternal gratitude.
36. Allah rewards me with more when I am appreciative.
37. I use rationality in my situation.
38. We ask for your help and praise you.
39. Continue to pray and provide the charitable donations that have been prescribed.
40. Whatever excellent you’ve saved for yourself will be found with God. To him, everything you do is evident.
41. God is Most Compassionate and Merciful when it comes to people.
42. “This gives you hope that Allah loves you and will forgive your transgressions.”
43. If I remember Allah, He will remember me.
44. When faced with affliction, those who declare, “We belong to Allah, and to Him, we shall return.”
45. I use rationality in my situation.
46. I make a list of three things for which I am grateful every night.
47. I seek Allah’s help through patience and prayer.
48. Allah emphasizes His Mercy more than any other characteristic.
49. I try to avoid getting into arguments.
50. My trials serve to bring me closer to Allah.
51. For me, the next planet takes precedence.
52. Without question, I am a believer.
53. I am reminded of Allah’s mercy.
54. Allah prays back to me when I pray to Him.
55. Gratitude and patience are two of my most basic emotions.
56. I take precautions and place my trust in Allah.
57. When I’m sad, I think of those who don’t have as much as I do.
58. Only beautiful things come out of my mouth.
59. I accept all the responsibility for my actions and seek Allah’s help whenever I require it.
60. We worship you and pray for your assistance.
61. Continue to pray and give the charity that has been prescribed.
62. You will find whatever good you have stored up for yourself with God. Everything you do is visible to him.
63. When it comes to people, God is Most Compassionate and Most Merciful.
64. “This will give you hope that Allah loves you and will forgive you for your mistakes.”
65. Allah will remember me if I remember Him.
66. I put my trust in Allah.
67. Life is packed with trials and tribulations. If I remain patient and remember Allah, everything will be well.
68. Allah wants to be merciful to me.
69. Allah is Forgiving, Righteous, and Generous.
70. If I ask Allah for pardon, He is the Most Merciful and Forgiving.
71. Allah appreciates my appreciation, and I understand Allah’s gratitude.
72. My life’s ambition is to draw closer to Allah.
73. I place my faith in Allah.
74. Life is full of tests. Everything will be well if I remain patient and remember Allah.
75. Allah wishes to show mercy to me.
76. Allah is Merciful, Just, and Generous.
77. If I seek forgiveness from Allah, He is the Most Merciful and Forgiving.
78. I am grateful to Allah, and Allah appreciates my gratitude.
79. My life’s goal is to become closer to Allah.
80. I make a list of three things for which I am grateful every night.
81. I seek Allah’s help through patience and prayer.
82. Allah will always emphasize his mercy more than any of the other characteristics.
83. I try to avoid getting into arguments.
84. My trials serve to bring me closer to Allah.
85. For me, the next planet takes precedence.
86. Without question, I am a believer.
87. I am reminded of Allah’s mercy.
88. Allah prays back to me when I pray to Him.
89. Gratitude and patience are two of my most basic emotions.
90. I take precautions and place my trust in Allah.
91. When I’m sad, I think of those who don’t have as much as I do.
92. Only beautiful things come out of my mouth.
93. If I ask Allah for pardon, He is the Most Merciful and Forgiving.
94. Allah appreciates my appreciation, and I understand Allah’s gratitude.
95. My life’s ambition is to draw closer to Allah.
96. Every night, I make a list of three things for which I am grateful.
97. Through patience and prayer, I seek Allah’s assistance.
98. Allah emphasizes His Mercy over all other qualities.
99. I always try to stay out of all possible fights as much as possible.
100. I accept responsibility for my own life and seek Allah’s guidance whenever I need it.
101. When I’m feeling stressed, I try to keep things as simple as possible.
102. My life’s purpose, I recall, is to adore Allah.
103. I put my trust in Allah’s mercy.
104. I pray to Allah first and foremost.
105. One of my favourite books is My Prophet.
106. I make every effort to remember Allah.
107. I start with myself when I want to make a difference in my life.
108. Exams are a part of life that cannot be avoided. I am patient when they arrive.
109. Allah is the source of my eternal gratitude.
110. Allah rewards me with more when I am appreciative.
111. I use rationality in my situation.
112. I make a list of three things for which I am grateful every night.






